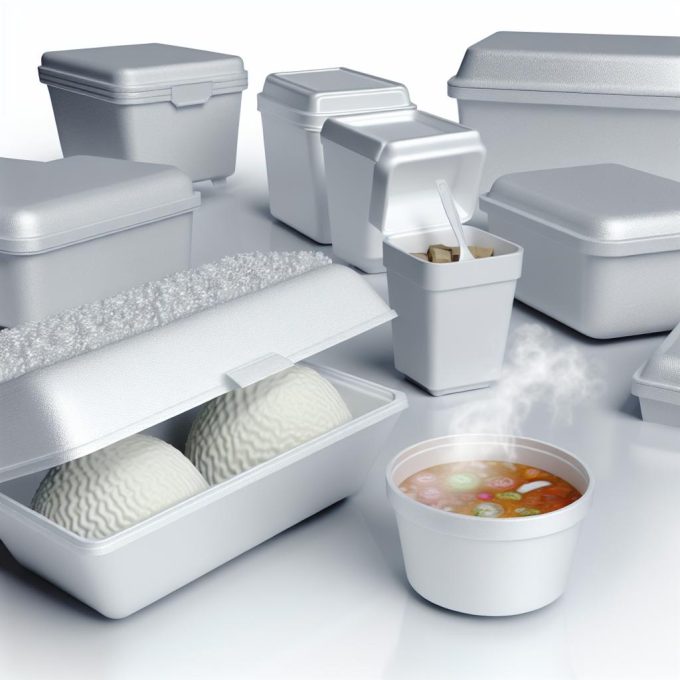
Introduction to Styrofoam Containers
Styrofoam containers, also recognized as expanded polystyrene (EPS), significantly contribute to the successful transportation of temperature-sensitive products. Their extensive usage in a variety of industries can be attributed to their superb insulating capabilities, lightweight properties, and cost-effectiveness. This article delves into the distinctive attributes of Styrofoam containers, their myriad applications, and the broader environmental considerations linked to their use.
Properties of Styrofoam Containers
Styrofoam manifests a unique array of properties tailored specifically for the preservation and thorough protection of temperature-sensitive goods. A notable composition characteristic of Styrofoam is that it consists predominantly of air, about 95%, which bestows it with exceptional insulation properties. This considerable air content is central to the material’s low thermal conductivity, a property that maintains consistent temperatures inside the container.
Insulation Efficiency
A pivotal advantage of Styrofoam containers is their impressive insulation efficiency. Given their structure, these containers markedly curb heat transfer, a vital feature when it comes to preserving the integrity of precious or delicate items such as pharmaceuticals, food products, and medical specimens during transit. By substantially insulating its contents from external temperature variations, Styrofoam ensures that goods maintain their requisite environmental conditions.
Lightweight and Durable
Another salient benefit of using Styrofoam containers lies in their lightweight yet durable design. This quality makes handling and transport a straightforward task, even leading to reduced transportation costs due to the lower weight. Despite their lightness, Styrofoam containers are robust enough to afford significant protection against physical impacts during transport, thereby safeguarding the contents.
Cost-Effectiveness
The economic aspect of Styrofoam containers also deserves attention. Compared to other materials that offer similar insulation capabilities, such as vacuum-insulated panels or refrigerated transportation solutions, Styrofoam stands out as a more economical option. This affordability enables businesses to optimize their logistics operations efficiently without endangering the quality or integrity of transported goods.
Applications of Styrofoam Containers
Given their flexible nature and varied attributes, Styrofoam containers find applications across an array of industries:
Pharmaceuticals
The pharmaceutical industry is one of the fields with a substantial reliance on Styrofoam containers. Medications and vaccines, which frequently necessitate stringent temperature control to preserve their efficacy, find an ideal companion in Styrofoam’s superior insulation properties. Ensuring that these medical products arrive at their destination without temperature-related degradation is crucial.
Food and Beverages
In the domain of food and beverages, the necessity of maintaining the cold chain is paramount, particularly for perishable items. Styrofoam containers provide a reliable solution to keep these goods at a required temperature, thus inhibiting spoilage and extending shelf life, which is particularly critical for fulfilling both commercial and safety standards in the food industry.
Cold Chain Logistics
Cold chain logistics, which involves overseeing the transportation of temperature-sensitive products through a supply chain, finds substantial benefit in Styrofoam containers. These containers play a crucial role in ensuring that the temperature confines are strictly adhered to from the point of origin to the destination, safeguarding product quality and compliance with regulatory standards.
Environmental Considerations
While Styrofoam containers present many advantages, there remain significant environmental concerns associated with their use. A notable issue is that EPS is not biodegradable, meaning it can linger in the environment for many years if not disposed of in an environmentally sound manner. Recognizing these environmental challenges, concerted efforts to develop and support robust recycling programs are underway. These initiatives aim to lessen the ecological footprint of Styrofoam and facilitate more sustainable waste management solutions.
Moreover, innovations are being explored, such as developing alternative materials that could potentially provide the same functional benefits as Styrofoam while being more environmentally friendly. Both industry leaders and environmental stakeholders advocate investing in research and development efforts to formulate solutions that harmonize economic and ecological interests.
Conclusion
In summation, Styrofoam containers are undeniably a vital element in the safeguarding and transportation of temperature-sensitive goods. Their high insulation efficiency, lightweight attributes, and cost-effectiveness solidify their standing as a favored choice across numerous industries. Nonetheless, the environmental challenges posed by their widespread use necessitate active discussion and action. Businesses are increasingly encouraged to invest in recycling initiatives while exploring and integrating sustainable alternatives whenever practicable. By adopting such a proactive stance, it is feasible to enjoy the advantages of Styrofoam while also addressing its environmental impact, thus promoting a balanced approach that aligns with both economic and ecological aspirations.